News
Oracle Tackles Spatial and Graph Big Data Analytics
- By David Ramel
- May 15, 2015
With nearly 20 years of experience working with spatial and graph data in its flagship relational database, Oracle Corp. is taking that expertise and putting it into a new Big Data tool.
Oracle Big Data Spatial and Graph is the new product that provides spatial and graph analytic services -- along with data models -- that support Big Data workloads running on Apache Hadoop and NoSQL databases.
The spatial component helps analyze data with location characteristics. For examples, it can determine if a location lies within a certain geographical area or how near one location is to others. It can also augment that data by filling in missing information, such as adding the city and state to a record that contains a ZIP code, for example.
The other primary component of the new product is a distributed property, in-memory, parallel, multi-user, graph analytics engine that includes 35 prebuilt analytics functions that help discover patterns and glean information from related data points. For example, it can analyze that data to come up with recommendations based on customer interests, behavior or published information such as social profiles. The graph capability works with Apache HBase and Oracle NoSQL databases, aided by a Groovy-based console.
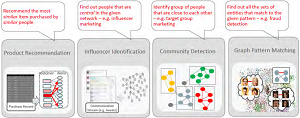 [Click on image for larger view.]
Common Graph Analysis Use Cases (source: Oracle Corp.)
[Click on image for larger view.]
Common Graph Analysis Use Cases (source: Oracle Corp.)
"Property graphs are commonly used to model and analyze relationships, such as communities, influencers and recommendations, and other patterns found in social networks, cyber security, utilities and telecommunications, life sciences and clinical data, and knowledge networks," Oracle said in a blog post announcing the product yesterday.
Oracle exec Peter Jeffcock also blogged about the new release, pointing out that, while the company hopes customers will use the new tool with other Oracle products -- such as the Oracle Big Data Appliance -- it can also be used by itself with Hadoop.
"We wanted to support the different kinds of data sets and the different workloads, which included being able to process this data natively on Hadoop and in parallel using MapReduce or in-memory structures," Jeffcock said. "Secondly, our overall Big Data strategy has always been to minimize data movement, which means doing analysis and processing where the data lies."
Oracle Big Data Spatial and Graph includes Java APIs -- such as TinkerPop Blueprints, Hadoop, NoSQL and HBase -- to access and analyze data. It supports large-scale vector- and raster-based processing and data visualization.
"Oracle Big Data Spatial and Graph represents a new opportunity for the Big Data platform," Oracle said. "By offering out of the box spatial enrichment services and analysis functions, as well as dozens of the most popular graph analysis functions, analysts and developers can now apply commercial-grade algorithms to their Big Data workloads."
About the Author
David Ramel is an editor and writer at Converge 360.