News
Hortonworks, IBM and Red Hat Team Up for Hybrid Containerized Big Data
- By David Ramel
- September 11, 2018
Hortonworks, IBM and Red Hat yesterday announced the Open Hybrid Architecture Initiative, seeking to provide a common enterprise deployment model to enable Big Data workloads to run across hybrid on-premises, multi-cloud and edge architectures.
The collaborative effort that incorporates open source components will employ several Hortonworks Big Data products along with the IBM Cloud Private for Data (a "unified data platform that accelerates your preparedness for AI"), to be used on the Red Hat OpenShift enterprise container and Kubernetes application platform.
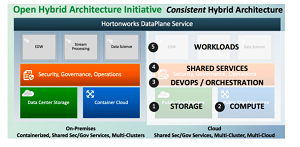
The intent is to shift Big Data workloads to a modern and container-based foundation, helping enterprises deploy Hortonworks and IBM platforms to a hybrid cloud environment powered by Red Hat OpenShift. Those aforementioned Hortonworks products include: Hortonworks Data Platform (HDP), an open source framework for distributed storage and processing of large, multi-source data sets; Hortonworks DataFlow (HDF), a scalable, real-time streaming analytics platform; and Hortonworks DataPlane (DPS), for the management, security and governing of data across hybrid environments.
"This initiative is a broad effort across the open-source communities, the partner ecosystem and Hortonworks platforms to enable a consistent experience by bringing the cloud architecture on-premises for the enterprise," Hortonworks said in a Sept. 10 blog post.
 [Click on image for larger view.]
Open Hybrid Architecture Initiative (source: Hortonworks)
[Click on image for larger view.]
Open Hybrid Architecture Initiative (source: Hortonworks)
The company said the Open Hybrid Architecture initiative will enable that by:
- De-coupling storage, with both file system interfaces and an object-store interface to data.
- Containerizing compute resources for elasticity and software isolation.
- Sharing services for metadata, governance and security across all tiers.
- Providing DevOps/orchestration tools for managing services/workloads via the "infrastructure is code" paradigm to allow spin-up/down in a programmatic manner.
- Designating workloads specific to use cases such as EDW, data science, and so on, rather than sharing everything in a multi-tenant Hadoop cluster.
The initiative will be enacted via a three-phase development process, with the first step being containerization of HDP and HDF workloads with DPS in a new interaction model to allow for the orchestration of workloads by programmatic spin-up/down of workload-specific clusters for users and workflows.
"In addition, Hortonworks will enhance HDP to adopt a cloud-native architecture for on-premises deployments by separating compute and storage and containerizing all Hortonworks Data Platform and Hortonworks DataFlow workloads," the companies said in a news release. "This allows customers to more easily adopt a hybrid architecture for Big Data applications and analytics, all with the common and trusted security features, data governance and operations that enterprises require."
About the Author
David Ramel is an editor and writer at Converge 360.