Here's a roundup of recent news in the Big Data space, featuring an expanded community edition of the NuoDB elastic SQL database, advanced in-database analytics on the GPU from Kinetica, a cloud native object storage server from Minio and more.
NuoDB Inc. today expanded the free community edition of its elastic SQL database aimed at developers. The enhanced NuoDB Community Edition features greater scale-out capabilities, the company said.
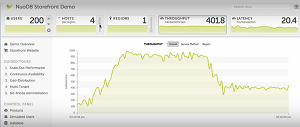
"Designed as an extendable, scale-out database, the newly released, expanded version of NuoDB Community Edition can automatically adjust to fluctuations and growth in transaction processing volumes while demonstrating resilience to hardware failure," NuoDB said in a statement today. "The latest version allows users to add additional transaction processing nodes to handle greater operational workload throughput and can be deployed across multiple hosts for fault tolerance and high availability."
 [Click on image for larger view.]
Testing Scale-Out and More in a Demo App (source: NuoDB YouTube video)
[Click on image for larger view.]
Testing Scale-Out and More in a Demo App (source: NuoDB YouTube video)
The community edition comes with certain limitations, including the use of up to three transaction engines and one storage manager. Previously, the free dev offering ("for those looking to research, deploy a database with a small project, or simply get started developing with our technology") lacked scale-out capabilities because it was limited to just one transaction engine and one storage manager on a single host.
NuoDB said the expanded community edition showcases:
- Highly available distributed database services across commodity servers.
- Application access via a single, logical database view.
- A standards-based SQL interface.
- In-memory, transaction handling.
- Elastic scaling of the transaction processing layer.
- ACID-compliance.
- Data persistence to a single host.
"When you're developing a commercial SaaS application, you want a database that can deliver elasticity and automation," the company quoted early customer William O'Keefe of Frenel Solutions as saying. "NuoDB's flexible distributed database is a powerful and interesting alternative to traditional SQL databases."
More information and a tutorial with installation instructions for a test project can be found in a blog post published today.
- Kinetica DB Inc. last week highlighted the advanced, in-database, GPU-powered analytics in version 6.0 of its namesake database.
In this latest edition the company introduced user-defined functions (UDFs), which enable advanced business analytics powered by GPU-accelerated data science logic on one database platform.
 [Click on image for larger view.]
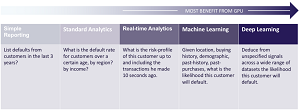
GPU Benefits Increase with Complexity (source: Kinetica)
[Click on image for larger view.]
GPU Benefits Increase with Complexity (source: Kinetica)
"[UDFs] enable compute as well as data-processing, within the database," the company said in a blog post. "Such 'in-database processing' is available on several high-end databases such as Oracle, Teradata, Vertica and others, but this is the first time such functionality has been made available on a database that fully utilizes the parallel compute power of the GPU on a distributed platform. In-database processing in Kinetica creates a highly flexible means of doing advanced compute-to-grid analytics."
Kinetica said its in-database processing capability especially benefits organizations that want to help line-of-business users -- as opposed to trained data scientists or highly skilled data developers -- to leverage advanced predictive analytics.
The company highlighted three such use cases:
- Vehicle design and testing: Vehicle manufacturers and sports teams collect millions of data points from wind tunnel runs and testing. These data points are used in thousands of calculations per run that typically take hours to process. UDFs will provide them the ability to perform on-demand calculations and adjust parameters in real time.
- Pricing and risk calculations: Financial institutions are merging more and more sources of data and need to run ever more sophisticated risk management algorithms and return results pre trade. UDFs will enable a next generation risk management platform that will also enable real-time drill-down analytics and on-demand custom XVA library execution.
- Genomics signaling: Pharmaceutical companies use genomics data to identify new signals and to accurately predict drug targets. Data is being ingested into Kinetica, Natural Language Processing (NLP) will be used to extract specific features and custom UDFs will be called to locate genome signals.
"As businesses move from deep analytics to predictive analytics, more and more operations stand to benefit from the parallel processing power of the GPU," Kinetica said.
-
Minio Inc. today unveiled its open source distributed object storage server, designed for cloud applications and DevOps shops.
The three-year-old Silicon Valley start-up says its flagship offering best suits the storage of unstructured data -- including photos, videos, log files, backups, container images and virtual machine (VM) images -- with object sizes ranging from a few kilobytes to 5TB.
 [Click on image for larger view.]
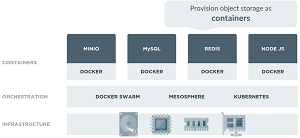
Cloud-Native Architecture (source: Wikimedia Commons)
[Click on image for larger view.]
Cloud-Native Architecture (source: Wikimedia Commons)
The object server was written in the Go programming language and released under an Apache v2.0 license. The offering's server, client and SDK can be downloaded here, and the code is also available on GitHub.
Selling points of the open source project include a light footprint that lends itself to being bundled in application stacks, like NodeJS, Redis and MySQL.
Other features of the object storage server highlighted by Minio include:
- Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3) compatibility: Minio supports both Amazon S3 v2 and v4 APIs. This compatibility allows applications to freely move between Amazon AWS and other cloud providers.
- Data protection: Minio withstands failure up to half the number of servers and drives using erasure-code and bitrot protection capabilities.
- Lambda functions: Minio supports Amazon AWS compatible lambda functions to perform useful actions like thumbnail generation, metadata extraction and virus scanning. Notifications are supported through various popular frameworks (AMQP, Elasticsearch, Redis, NATS, WebHooks, Kafka and Postgres) and natively over HTTP long-polling.
"The solution enables applications to manage massive quantities of unstructured data, and enables cloud and SaaS application developers to adopt emerging cloud hosting providers such as Digital Ocean, Packet and Hyper.sh with Amazon S3 like capabilities," the company said in a statement today. "Minio's object storage server is now production ready, with major features such as erasure code, bitrot detection and lambda notification, and has grown in popularity amongst the Docker, Mesos and Kubernetes communities due its cloud native architecture."
Intel Corp. recently open sourced its own Big Data offering. BigDL, a distributed deep learning library that runs on Apache Spark, is now available on GitHub.
"Users can write their deep learning applications as standard Spark programs, which can directly run on top of existing Spark or Hadoop clusters," the project site said.
Intel said the library is especially useful for organizations that want to perform analytics on large amounts of data stored -- in HDFS, HBase, Hive and so on -- in the same Hadoop or Spark cluster where that data resides. Also, it facilitates the addition of deep learning capabilities -- such as training or prediction -- to existing Spark programs or workflows. Yet a third use case is organizations that want to put existing Hadoop or Spark clusters to use running deep learning applications that can subsequently be shared with separate workloads such as ETL, data warehouse, feature engineering, classical machine learning, graph analytics and so on.
Highlighted features include:
- Rich deep learning support. Modeled after Torch, BigDL provides comprehensive support for deep learning, including numeric computing (via Tensor) and high level neural networks; in addition, users can load pre-trained Caffe or Torch models into Spark programs using BigDL.
- Extremely high performance. To achieve high performance, BigDL uses Intel MKL and multi-threaded programming in each Spark task. Consequently, it is orders of magnitude faster than out-of-box open source Caffe, Torch or TensorFlow on a single-node Xeon (that is, comparable with mainstream GPU).
- Efficient scale-out. BigDL can efficiently scale out to perform data analytics at "Big Data scale", by leveraging Apache Spark (a lightning fast distributed data processing framework), as well as efficient implementations of synchronous SGD and all-reduce communications on Spark.
More information -- such as tutorials, examples and a programming guide -- is available on the project's documents page.