News
Application Development Research Predicts Low-Code Tooling Takeover
- By David Ramel
- August 12, 2019
Low-code development tools, having grown and matured during a time of increased enterprise app demand and a programming skills shortage, will be used for most application development by 2024, research firm Gartner Inc. predicts.
The firm made the prediction in its latest report on the low-code movement, which uses rapid-application development techniques to help "citizen" or "ordinary business user" developers crank out enterprise apps without having to know a lot about programming.
Gartner's new "Magic Quadrant for Enterprise Low-Code Application Platforms" examines 18 low-code vendors leading the charge to unskilled dominance.
"By 2024, three-quarters of large enterprises will be using at least four low-code development tools for both IT application development and citizen development initiatives," the report said. "By 2024, low-code application development will be responsible for more than 65 percent of application development activity."
The company's definition for such tools is: "A low-code application platform (LCAP) is an application platform that supports rapid application development, one-step deployment, execution and management using declarative, high-level programming abstractions, such as model-driven and metadata-based programming languages. They support the development of user interfaces, business logic and data services, and improve productivity at the expense of portability across vendors, as compared with conventional application platforms."
Gartner said its research resulted in the following insights that can provide a business case for using low-code application development platforms:
- Organizations sought an LCAP mainly for its application productivity benefits, reduced time to market and ability to improve business process automation.
- Most used an LCAP for both enterprise and departmental applications, which more than half deployed organization-wide.
- Less than half of their LCAPs were used to support process automation or multiexperience development.
LCAPs improve productivity, citizen development and the end-user experience.
- LCAPs are primarily cloud or aPaaS offerings, but significant deployments are self-managed on-premises or on customers' own cloud contracts. Some are a hybrid of cloud and on-premises deployments.
- The skills required and application delivery times for LCAPs are low, compared with historical norms for application development.
The low-code report is aligned closely with the firm's recent first-ever publication of "Magic Quadrant for Multiexperience Development Platforms" report, renamed to reflect less of a mobile-centric focus.
In fact, vendors OutSystems, Mendix and Salesforce were placed in the "Leaders" quadrant in both reports. In the new low-code report, they're joined by Microsoft and Appian, also familiar figures in mobile development.
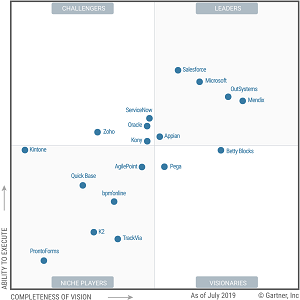 [Click on image for larger view.]
Magic Quadrant for Enterprise Low-Code Application Platforms (source: Gartner)
[Click on image for larger view.]
Magic Quadrant for Enterprise Low-Code Application Platforms (source: Gartner)
"The enterprise LCAP market is growing strongly, due to continued demand for applications and a shortage of skilled developers," Gartner said in its report market overview. "Low-code development is a natural evolution of rising abstraction levels in application development, which will eventually lead to viable cross-enterprise, highly scalable citizen development and composition of applications.
"LCAP vendors represent the vanguard of the movement to democratize application development by increasingly replacing standard business application development in Java or .NET, and providing differentiating alternatives to commercial off-the-shelf or SaaS applications."
About the Author
David Ramel is an editor and writer at Converge 360.